Everything you need to know about clean energy
What does clean energy mean?
Defining what clean energy is, is arguably one of the most important questions of our generation. A clean energy source must be one that humanity can rely on for living and growing without jeopardizing its own future. Clean energy can be defined by the following four criteria:

Clean
Firstly, clean energy must ensure a clean sky and unpolluted soil to maintain the viability of our planet. This criterion is essential for sustaining the natural cycles.

Safe
Clean energy must be secure. It should not pose additional risks for the future, and it should be safe for human use. Ensuring safety is paramount to public acceptance and trust in clean energy sources.

Available
Clean energy must also be readily available when needed. Trust in the availability of energy is crucial for reliance on clean energy solutions. The more you plan for the future, the greater the need for reliability in your energy sources.
Abundant and Affordable
Finally, clean energy should be abundant and affordable. If an energy source cannot be feasibly accessed or utilized, it becomes ineffective. To foster a sustainable future, clean energy must be accessible to as many people as possible. Only under these conditions can clean energy serve as a lever for sovereignty.
The most common sources of clean energy and how they work
No single energy source currently available on Earth meets all the criteria identified above. Does that mean we do not have clean energy options available today? Not at all. We have a diverse mix of clean energy sources that we can rely on to mitigate carbon emissions from fossil fuels. These sources are known as “carbon-free sources,” meaning they do not emit carbon dioxide during their usage, unlike oil, natural gas, or coal. The main types of clean energy include:
This source harnesses the power of the wind. When the wind blows, it causes a turbine to spin, which generates electricity for the grid. The stronger the wind, the more electricity is produced. However, wind energy is considered an intermittent source because it is dependent on wind strength.
This source utilizes the power of the sun. Solar energy is converted into electricity using photovoltaic cells. More sunlight means more electricity. Like wind energy, solar energy is also intermittent, as it depends on weather conditions and the day-night cycle.
This energy source takes advantage of gravity’s effect on water. As water flows downward, it turns a turbine that generates electricity. The availability of hydropower is contingent upon water supply, making it highly dependent on geographical location and climate, particularly in dry conditions.
Biomass energy comes from the direct combustion (burning), thermochemical conversion, chemical conversion, and biological conversion of organic materials to produce heat, gas, or liquid fuel. These organic materials include wood, agricultural crops, waste materials, biogenic materials in municipal solid waste, animal manure, and human sewage. While biomass is not classified as a fossil fuel, it does emit carbon during combustion, and its contribution to the energy mix remains relatively low.
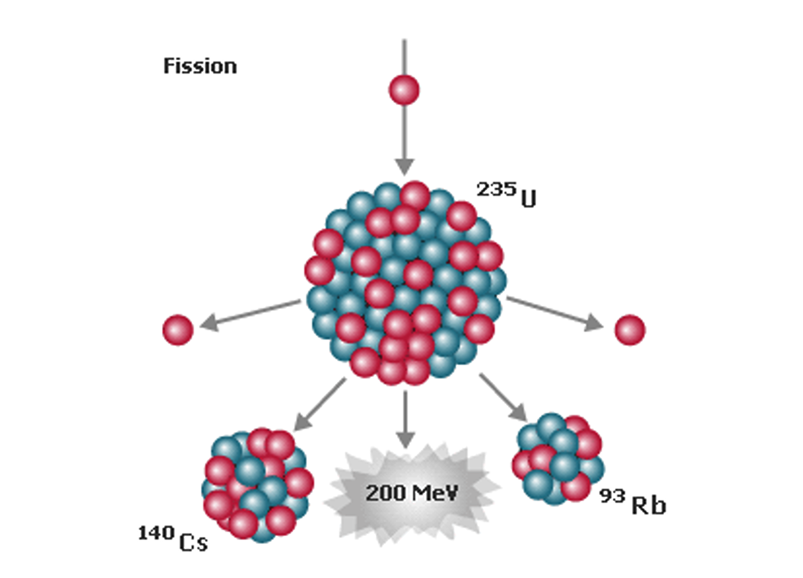
Is nuclear energy clean? Yes, it is classified as a carbon-free energy source. However, nuclear energy must be handled with care, which is why traditional nuclear power plants have restrictions regarding population density and seismic risks. Nuclear energy is derived from the relationship between mass and energy (E=mc²). In the process of nuclear fission, splitting a heavy atom of uranium into lighter atoms (such as rubidium and cesium) can produce up to a million times more energy than the same quantity of coal. Due to the potential for chain reactions, it requires a significant amount of safety measures to ensure operational security, as evidenced by incidents like the Chernobyl and Fukushima nuclear accidents. Additionally, the waste produced from nuclear fission remains highly radioactive and must be managed cautiously to protect public safety. The picture below describes what fission is at atom level.
For each source of clean energy, clean energy companies deploy dedicated facilities regarding the advantage of the location and the safety rules.
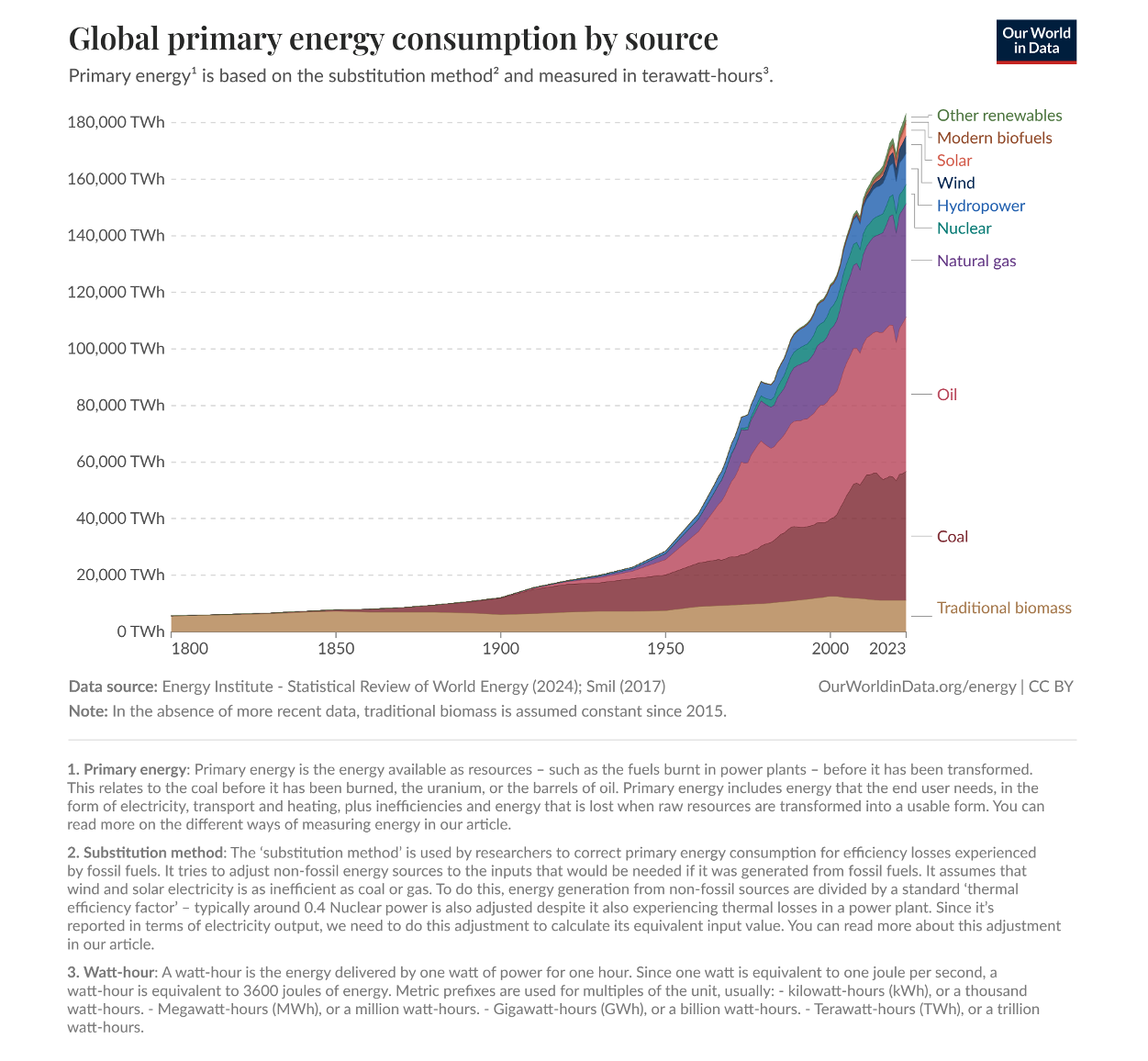
Here after a graphic that represents the share of the different energies (clean and not clean) into the worldwide energy consumption. Clearly, clean energy sources represent a very small part of the global energy consumption. That means that the current way the clean energy sources are managed is ineffective regarding the share of the fossil fuel they need to replace. The current paradigm of the clean energy sources needs to be changed to foster the right clean choice energy.
Advantages of clean energy
Clean energy experts highlight the advantages of clean energy through the three letters “E,” “S,” and “G”:
E: Environment
Clean energy sources do not deplete natural resources, promoting a sustainable world.
By respecting the environment, humanity can confidently rely on clean energy for a safer future.
S: Society
Society expects growth to enhance quality of life. Clean energy can be scaled to support this growth effectively. It also needs to be abundant and affordable to stimulate economic development and industrialization.
Furthermore, clean energy enables new applications in a sustainable world, such as artificial intelligence (AI), which requires substantial energy resources.
G: Governance
Clean energy promotes better governance and energy sovereignty, necessitating independence and autonomy in energy supply.
How can clean energy can be used?
Clean energy offers at least three primary ways to be utilized:
Clean electricity is primarily generated from sources such as nuclear power plants, windmill, hydropower, and solar panels. Its applications include:
- Domestic Use: Lighting, heating, clean energy charging batteries, phones, computers, air conditioning, and more.
- Industry: Powering computers, operating machinery, high-temperature processing, and material cutting.
- Transportation: Electric trains and electric vehicles.
- Communication: Supporting radio transmissions, fiber optics, and copper cable networks.
Clean heat is predominantly produced by nuclear power plants and biomass sources. Its applications encompass:
- District Heating: Providing centralized heating to multiple buildings or areas.
- Industrial Processes: Used in chemical transformations, cooking, and other industrial applications.
Primarily derived from biomass sources, clean chemical energy includes:
- Liquid Fuels: Used for various applications, including transportation and heating.
- Gaseous Fuels: Employed in heating and energy generation.
How clean energy can reduce global warming?
Global warming is primarily due to the enhanced greenhouse effect, which is caused by the increasing concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. In other words, the less carbon dioxide you produce, the more you help mitigate global warming.
Therefore, replacing fossil fuels such as oil, coal, and natural gas—which emit carbon when burned—with clean energy sources that are carbon-free will contribute to reducing global warming.


GenF’s vision about the future of clean energy
In a few decades, it will be almost impossible to identify how to store nuclear waste due to the unacceptability among citizens who do not want these waste facilities near them.
We cannot rely solely on intermittent energy sources such as solar panels or windmill because ineffective a part of the time.
Another energy source has existed since the beginning of time: the energy of the stars, also known as fusion energy, is now becoming accessible.
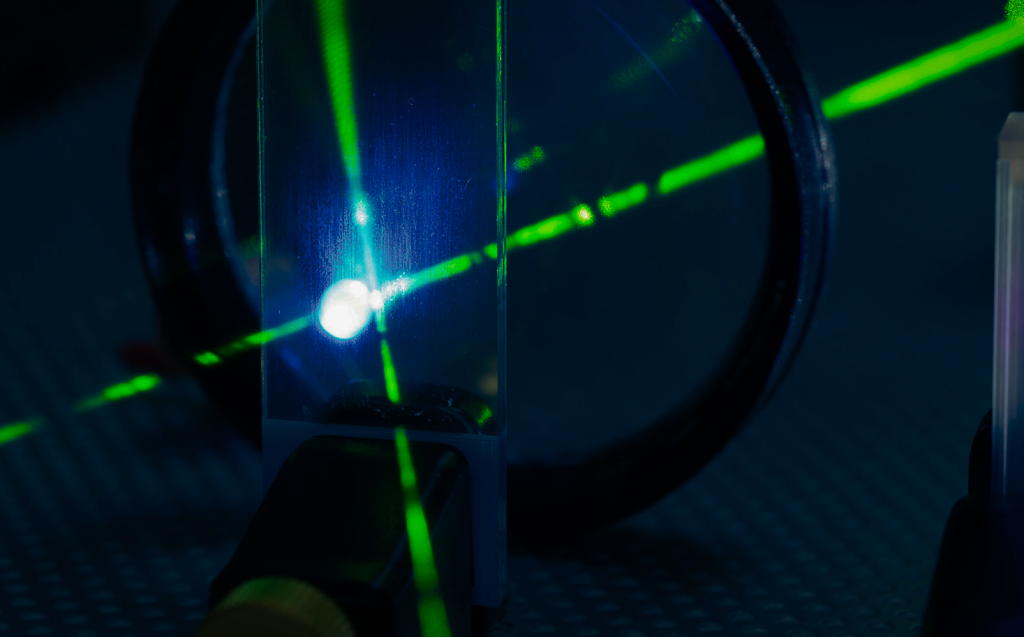
Since December 2022, following the demonstration by the National Ignition Facility, humanity knows that net positive energy can be achieved through laser-induced processes. This demonstrated fusion reaction using lasers is referred to as Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF).
ICF meets all the criteria for clean energy.
GenF is industrializing Inertial Confinement Fusion through a unique and collaborative partnership with the French Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) and the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS).
GenF plans to market the first ICF reactor by 2040 and aims to deliver the first megawatt to the energy grid by 2050.

Contact us
Do you have any questions? Don’t hesitate to write to us.
We’re here to help!




